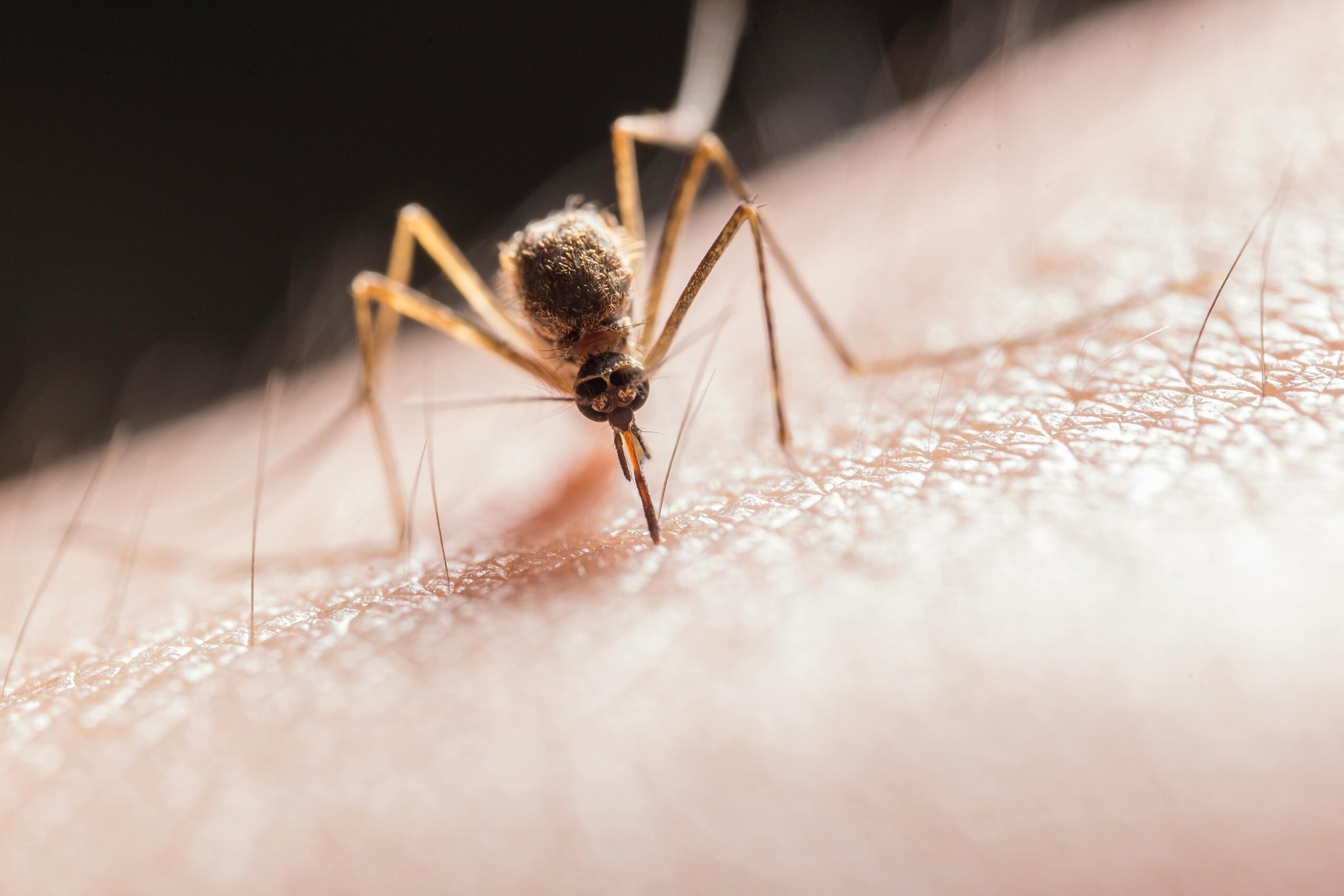
As the natural world awakens with the warmth of the seasons, so too do the populations of ticks and mosquitoes, stirring concerns about their potential as vectors for disease. A nuanced understanding of their lifecycles, behaviors, and preferred habitats is essential in crafting proactive strategies for their control. It is crucial to mitigate the immediate nuisance these pests present and address the broader public health implications they carry.
Key Takeaways:
- Understanding the lifecycle of ticks and mosquitoes is crucial for effective prevention and control.
- Knowledge of preferred habitats allows for targeted strategies to minimize their populations.
- Both environmental changes and personal preventive actions are essential in reducing health risks.
The Hidden Life of Ticks: From Larvae to Adults
A tick’s lifecycle unfurls through several stages, beginning with the egg, transitioning through larval and nymph phases, and culminating in adulthood. Each stage ushers in different behavioral patterns and risks. For instance, nymphs are known for being particularly active during the spring, which coincides with increased human outdoor activity—thus heightening the risk of transmission of diseases such as Lyme disease. As ticks develop, they seek larger hosts, which can lead to more frequent encounters with humans and their pets. Through informed and attentive Maine tick and mosquito control, one can significantly diminish the threat these tiny but formidable creatures can pose to our well-being.
Mosquito Populations and Their Seasonal Cycles
Consistently driven by temperature and moisture, mosquitoes experience population booms that typically align with the warmer and wetter seasons. This is due to their reproductive cycle, which flourishes in standing water—from marshes to artificial containers, any stagnant water body can serve as a potential breeding ground. The challenge thus becomes identifying and addressing these water sources, whether they are apparent, like a neglected pool, or often overlooked, such as a rain-filled flowerpot. The key lies in preemptive action, taken before these insects have the chance to mature and propagate, ultimately reducing the instances of mosquito-borne illnesses.
Habitats of Concern: Where Ticks and Mosquitoes Thrive
Both ticks and mosquitoes demonstrate a strong preference for environments that offer ample protection and sustenance. Ticks find refuge in the leaf litter of wooded areas and tall grasses, where they can patiently await the passage of suitable hosts. Mosquitoes, contrarily, are more ubiquitous but still show preferences for areas in proximity to still water sources. If not carefully maintained, our regular domestic landscapes can inadvertently become havens for these pests. Implementing strategies such as landscaping to disrupt ideal habitats and timely removal of standing water can deter their establishment close to our homes.
The Role of Climate and Weather in Pest Populations
Climate changes have direct and palpable effects on the habitats and lifecycles of ticks and mosquitoes, often exacerbating the problems they present. Warmer temperatures can elongate these pests’ lifespan and breeding seasons, thereby increasing their numbers and the duration of their threat. Unusually mild winters may not sufficiently curtail pest populations, leading to an early and robust emergence in the spring. Managing the resultant surges in tick and mosquito activities calls for an adaptive and forward-thinking approach that considers the long-term trajectory of our climate.
Health Risks Associated with Ticks and Mosquitoes
A tick or mosquito bite does more than merely irritate the skin—it can be a conduit of severe illnesses. Ticks are notorious carriers of lyme disease, while mosquitoes can transmit many viruses, including but not limited to West Nile and Zika. Each of these diseases carries with them a range of symptoms and potential long-term health ramifications. It is crucial, therefore, to incorporate a regimen of preventive measures into our outdoor routines, especially during times and in areas where these pests are known to be prevalent. The World Health Organization emphasizes the impact of these vector-borne diseases and the importance of coordinated efforts to minimize their spread.
Natural vs. Chemical Control Methods: Pros and Cons
In pursuing tick and mosquito mitigation, we face various control methods, each with advantages and disadvantages. Natural remedies, like using essential oils or introducing predators such as certain fish species into water bodies, can reduce pest populations without the collateral damage often associated with synthetic chemicals. Chemical repellents, although potentially more effective in the short term, raise concerns regarding their environmental impact and potential health risks. Deciding between these approaches—or whether to employ a combination—requires carefully assessing the specific circumstances and understanding the broader ecological consequences.
Tick and Mosquito Surveillance and Control Programs
Public health authorities often initiate surveillance and control programs to monitor the prevalence of ticks and mosquitoes and curb their growth. These programs can entail the widespread application of control measures, public education campaigns, and research into the epidemiology of pest-associated diseases. By staying informed about these initiatives and participating where possible, we can contribute to a collective defense against the threats posed by ticks and mosquitoes.
Preventative Measures: Protecting Yourself and Your Family
The adage “prevention is better than cure” is particularly apt regarding tick and mosquito bites. Simple preventive methods can include wearing light-colored, long-sleeved clothing in areas known for high pest activity, applying insect repellent recommended by health authorities, and conducting routine body checks after outdoor activities. Regular tick and flea treatments are essential for those with pets, as animals can unknowingly bring these pests close to family members. Strong vigilance and routine practices form the cornerstone of personal protection against ticks and mosquitoes.
Emerging Research and Innovations in Pest Management
Scientific research continually sheds light on innovative approaches to pest control. These range from genetic editing techniques to reduce mosquito fertility to developing novel biopesticides targeting pests while leaving other wildlife unharmed. As research presses forward, it illuminates paths that could revolutionize how we mitigate the risks associated with ticks and mosquitoes. It bodes well for our future ability to manage these pests in ineffective and environmentally conscious ways.
In conclusion, you can significantly reduce exposure to these pests and their associated health risks by applying knowledge about tick and mosquito lifecycles and habitats, adopting seasonal and environmental management strategies, and staying updated on the latest research. Combining personal protective measures with broader, community-oriented approaches offers our best chance at mitigating the complex challenges that ticks and mosquitoes present.