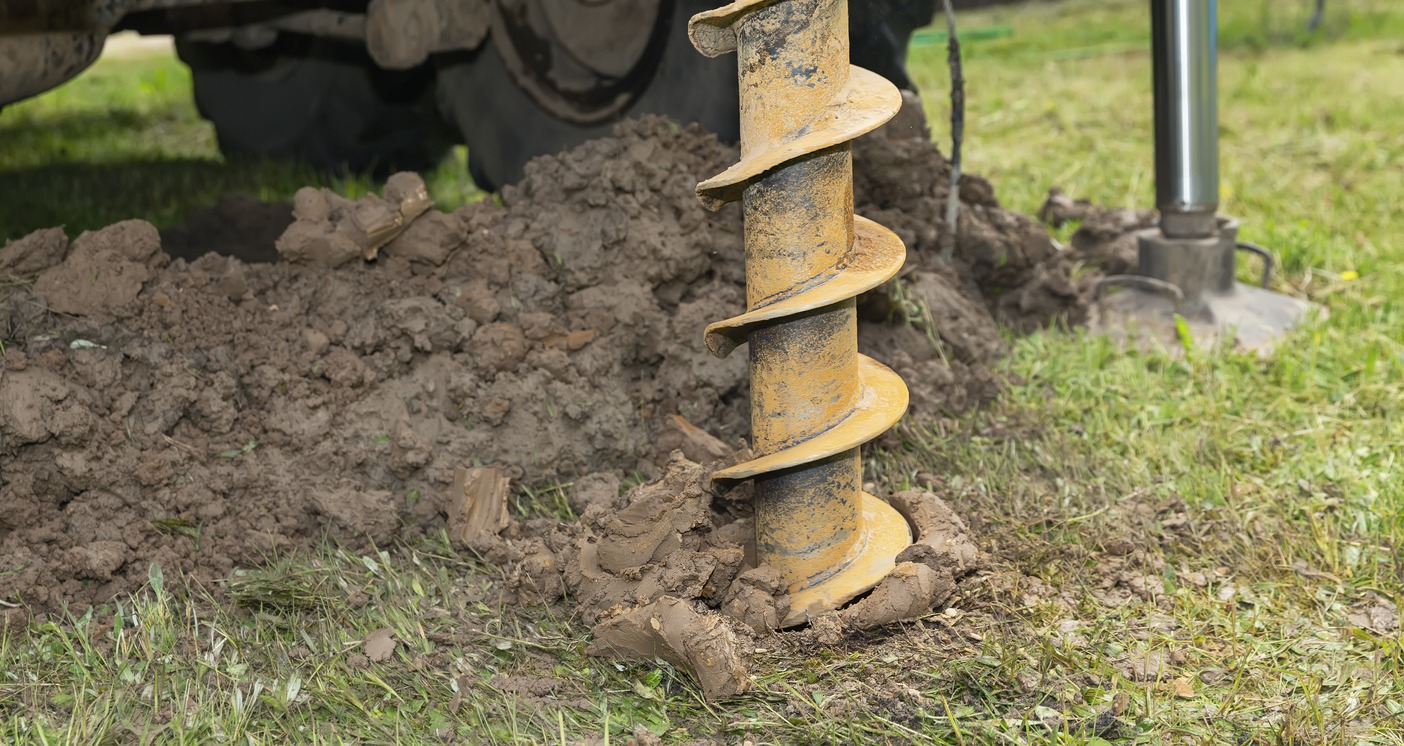
A well or a water well is a man-made structure that is either dug, drilled, driven, or bored into the ground to provide people access to groundwater sources. It is designed to extract water from underground aquifers for different reasons, such as for irrigation, drinking water, or industrial use. For homeowners, water wells can provide a reliable and independent source of clean and potable water, particularly if you are living in areas where access to a municipal water supply is unreliable or limited.
Many farmers also use water wells for agricultural irrigation. In fact, they are important as they provide water to sustain crop growth and support other agricultural activities, which ensure food security and sustainable farming practices. In addition to that, water wells are also used to supply water to different industrial processes, such as construction, manufacturing, and commercial operations. Wells can also serve as an important resource during emergencies, natural disasters, or when there is scarcity in water, being used as a backup water supply when other sources are not available or are disrupted.
In this article, we are going to provide you with the different types of water wells. This way, we will be able to decide what the most suitable type of water well is for a particular purpose or location. If you are interested, read on and learn about the different types of wells.
This is a great option if you are looking for used Borehole Drilling Contractors Hampshire.
Dug Wells
Dug wells are also called hand-dug wells or traditional wells. They are built by excavating the ground manually until the water table is reached. This type of well has been used for centuries, and it is the simplest and most available method of accessing groundwater. But it is labor-intensive and time-consuming to build a dug well.
Most dug wells are shallow, ranging from a few feet to around 30 feet deep. The depth of a dug well is limited by the manual labor used in digging. But they have a wider diameter of around 3 to 10 feet, which allows easier access for maintenance and water extraction.
This type of water well uses natural filtration from the layers of rock and soil surrounding the well shaft. These layers work as a filter, removing some impurities from the groundwater. However, since dug wells are shallow, they are more susceptible to contamination from surface water, seepage, runoff, or pollutants. It is important that a dug well has proper sealing and maintenance to minimize the risks of contamination.
Most dug wells are used in rural communities with limited access to water sources. They can also be used to provide water for domestic use, livestock watering, and small-scale irrigation in suitable areas and hydrological conditions.
Advantages
- Dug wells are less expensive to build as they need minimal equipment and machinery.
- They can be constructed in places with limited resources and where drilling equipment may not be available.
- Dug wells are easy to maintain and repair as their wide diameter makes them easy to access.
Disadvantages
- Dug wells are not suitable in places that have deep water tables as they are often shallow and may not reach enough water sources.
- Dug wells are more prone to contamination from bacteria and surface pollutants.
- Dug wells depend on the geology of the area. If the area has hard rock or clay soils, it can make excavation difficult or sometimes impossible.
Drilled Wells
Drilled wells are built by using drilling equipment to bore through the surface of the earth and reach underground water sources. These wells are often used to access deeper and more reliable water reservoirs. They can reach greater depths compared to dug wells, ranging from a few dozen to several hundred or even thousands of feet deep, depending on the water table and geological conditions. However, they have narrower diameters than dug wells, from a few inches to a foot or more in order to maintain the integrity and stability of the well shaft.
Most of the time, drilled wells are lined with steel casing to prevent them from collapsing and to maintain their integrity. The casing is inserted into the drilled hole and sealed to prevent it from being contaminated. Aside from that, drilled wells also usually have a pumping system, such as a jet pump, to extract water from the underground aquifer and deliver it to the surface. To make drilled wells, specialized drilling equipment is needed, such as rotary drilling rigs or percussion drilling machines, operated by trained professionals.
Advantages
- Drilled wells can access deeper aquifers, providing access to more abundant and reliable water sources.
- The steel casing of drilled wells gives protection against surface water contaminants and pollutants.
- Drilled wells can yield larger quantities of water than dug wells.
- Drilled wells can last longer than dug wells as long as it is constructed properly and maintained well.
Disadvantages
- Building drilled wells are more expensive as more complex equipment, skilled labor, and materials are needed.
- Drilling and constructing a well also need specialized knowledge and professional drilling services, which may add to the cost of the water well.
- Geological conditions like hard rock and complex subsurface structures may make the process of drilling challenging, which may increase costs and time.
Driven Wells
Driven wells are also called sand-point wells or screened wells. They are made by driving a pipe or casing into the ground to access shallow water sources. They are also commonly used in places with sandy or gravelly soils. A driven well is typically shallow, ranging from around 10 to 50 feet deep. It also has a relatively small diameter, which is only around 2 to 6 inches, which helps in driving the pipe or casing into the ground. The lower section of a driven well’s casing is fitted with a screen or perforated pipe to enable water to enter while filtering out sediment and debris.
To install a driven well, a driving mechanism, like a heavy hammer or pile driver, is used, forcing the casing into the ground. The casing is driven until it reaches the desired depth. This type of well is usually used as a residential water supply, small-scale irrigation, and non-potable water needs in places with suitable soil conditions. A driven well is also a great option for accessing water in sandy coastal areas or regions that have shallow water tables.
Advantages
- Driven wells are less expensive to install compared to drilled wells as it needs simpler equipment and less labor.
- The installation process for a driven well is fast and simple, particularly in places with suitable soil conditions.
- They are effective in accessing shallow water sources, making them a viable option in areas with high groundwater levels.
Disadvantages
- Driven wells are not made for accessing deep water sources, making them not suitable for areas with low water yields.
- The screens or perforations in driven wells are prone to clogging from sediment or fine particles. It needs regular cleaning and maintenance.
- Driven wells are only best for sandy or gravelly soils and may not be suitable in places with clay or compacted soils.
Bored Wells
A bored well is also sometimes referred to as an augered water well. It is made by using a piece of specialized drilling equipment called an auger to bore into the ground. It is a common method used for building shallow wells. Bored wells are often shallow, ranging from a few feet to about 100 feet deep. They are made to access groundwater sources that are closer to the surface. They have a larger diameter compared to drilled or driven wells, which range from 6 to 36 inches, allowing greater water flow and easier casing installation.
Bored wells are made by rotating an auger bit into the ground to cut and remove soil or rock. The process continues until the desired depth is reached. After the well is drilled, a casing is inserted into the borehole to prevent collapse and maintain the integrity of the well. The casing is also sealed to prevent contaminants from entering the well. This type of well is commonly used for residential water supply, small-scale irrigation, and non-potable water needs in places that have shallow water tables and suitable soil conditions.
Advantages
- Bored wells can be installed fast, particularly in areas with suitable soil conditions.
- They are effective for accessing groundwater sources in shallow water tables, where drilling deeper wells may not be needed.
- Bored wells are more cost-effective than drilled wells, as they need simpler equipment and less labor.
Disadvantages
- Bored wells are not suitable for accessing deep water sources. They are mainly used for shallow groundwater extraction.
- The effectiveness of bored wells depends on the conditions of the soil and rock. For instance, hard rock or dense clay may hinder the drilling process or limit the water flow.
- Just like other shallow wells, bored wells are also vulnerable to contamination from surface water runoff or pollutants. Proper sealing and maintenance are needed to keep the water quality good.
Subcategories of Water Wells Based on Water Source
In addition to those main types of water wells we’ve mentioned above, wells can also be categorized based on the water source. Read on below to learn more about these:
Surface Water Wells
Surface water well is made to extract water from nearby surface water sources, such as lakes, rivers, or reservoirs. It usually has intake structures that draw water directly from the surface water body. But water from this type of well needs to be treated extensively, which includes filtration and disinfection, in order for it to meet drinking water standards. Most surface water wells are used in municipal water supply systems and other large-scale operations that are located near surface water sources.
Groundwater Wells
These wells are made to access water stored in underground aquifers. A groundwater well taps into the natural underground reservoirs of water found in permeable rock or soil formations. It is high quality, but may still need testing and treatment based on local conditions. This type of water well has diverse applications, such as for residential water supply, agricultural irrigation, and industrial water needs.
Confined Aquifer Wells
A confined aquifer well is drilled into confined aquifers, which are underground water-bearing formations sandwiched between impermeable layers. This type of well is often under pressure, allowing the water to rise above the level of the aquifer.
There are times when some confined aquifer wells are classified as artesian wells, which are characterized by natural artesian pressure that causes the water to flow to the surface without pumping. This type of water well can provide a reliable and pressurized water source for different purposes, such as residential, commercial, and agricultural use.
Unconfined Aquifer Wells
This type of well is drilled into unconfined aquifers, which are water-bearing formations with permeable layers extending to the surface. The water level in this type of well can fluctuate based on different factors, such as precipitation, groundwater recharge, and seasonality. Unconfined aquifer wells are also called water table wells because they access water at the level of the water table. They are mostly used for domestic water supply, small-scale irrigation, and local community water systems.
Conclusion
It is important to understand the various types of water wells in order for us to choose the right method to access groundwater or surface water sources. By understanding the characteristics, advantages, and limitations of each type of well and considering the source of water, one can make informed decisions regarding well construction, maintenance, and water usage.
Overall, selecting the most suitable type of well and understanding its specific requirements contribute to the efficient and effective utilization of water resources, meeting various needs ranging from residential water supply to agricultural and industrial applications. We hope this article helped you learn more about the different types of wells.